When it comes to data center cabling, there are various variables to consider. How do you run your cable? What kind of cable should you get? How can you design the most efficient system? Here are some recommended practices for arranging your data center cabling needs.
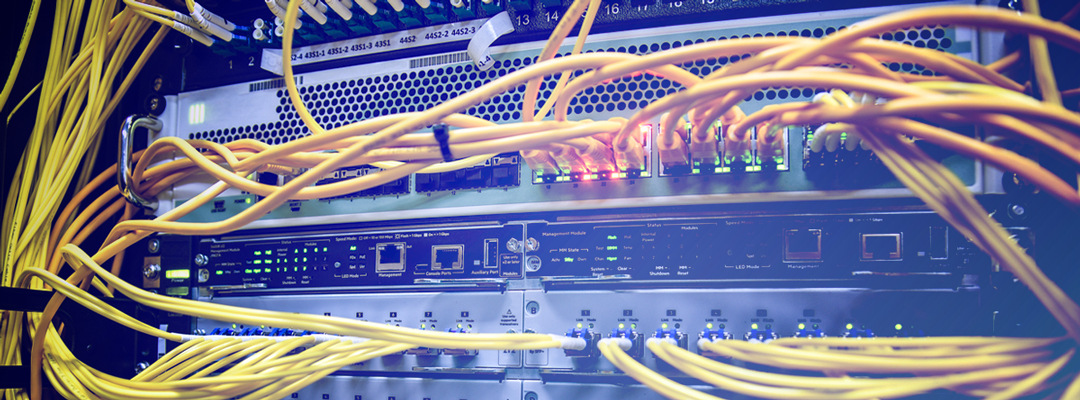

- Properly label cables.
Organizing and labeling your cables is arguably the most essential and simple practice to undertake. Labels make troubleshooting easier and cable tracing faster, reducing downtime and increasing productivity. Attaching legible labels to each cable, utilizing a commercial-grade label, color-coding labels, and adhering to a labeling standard such as ANSI/TIA 606-B are all good labeling practices. - Ensure cables aren’t blocking airflow.
Remove any unneeded or abandoned cables from beneath the raised floor or inside your cabinets. These excessive cables will obstruct airflow and result in higher temperatures, which might create downtime or waste energy caused by ineffective cooling. - Maintain cable cooling.
It is generally understood that a data center must keep its equipment cold, but it is often ignored that cables can grow warm if there is a lot of cabling. Install and monitor temperature sensors to guarantee optimum cooling of all cables and equipment. - Make use of cable management.
Cable raceways, cable rings, and cable ties are great for neatly bundling cables and making their paths easy to follow. Remember to run cables horizontally to the rack, bundle them, then twist your bundle and run it vertically. - Understand where to install cables.
In a smaller data center where equipment is not routinely changed, cable trays can be mounted directly to the top of racks. Larger data centers, on the other hand, will benefit from suspended cable pathways from the ceiling. This allows you to move or install racks without having to reroute cable connections. - Use patch panels.
Patch panels help you keep large amounts of cables organized and allow for greater flexibility of your network infrastructure. They can be mounted within racks and include blank ports on one side and a termination point on the other. Cables can easily be terminated, labeled, and patched into your network hardware. - Maintain accurate documentation.
Keep detailed records of your cabling components, such as compatible cable types, cabinet elevations, connectors, and the number of data and power ports. Thorough documentation can reduce troubleshooting time and assist those who later work on the data center that wasn’t involved in planning or installation. - Plan for the future.
Data centers are constantly evolving to accommodate changing technology and expanding demands. Successful data center management strategies can help to support future growth by making dynamic IT equipment provisioning simple. Focusing your planning solely on current demands will result in increased expenses and inefficiency in the long run.